Colon adenocarcinoma is the most widely diagnosed gastrointestinal cancer, that primarily affects men and women over 50 years of age. Read on to learn more.
The digestive tract or the digestive system of vertebrates has a lot of complex parts and processes, vis-à-vis vertebrates, and the colon is a crucial part of this digestive system. It is the last, or the lowest portion of the digestive system, and its task is to extract salt and water from any solid waste material that is about to be released by the body. The colon is a part of the large intestine, and is situated just above the rectum and the anus. Any waste material that passes through the body will be regulated by it.
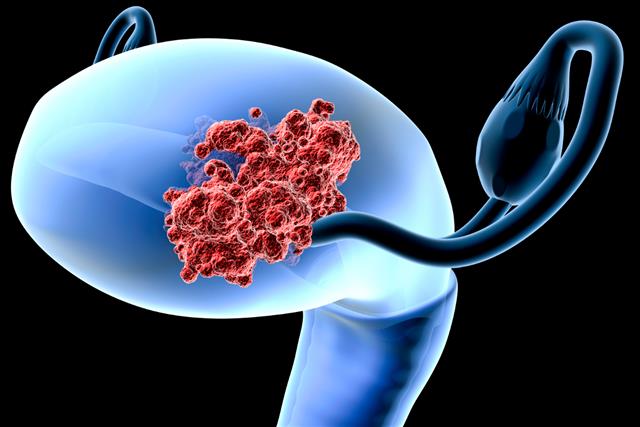
What is Adenocarcinoma of the Colon?
This is a cancer that affects the colon or the rectum. Basically speaking, this is a gastrointestinal cancer, and statistically this is the most common gastrointestinal cancer across the world. The cancer originates in the inner walls of the colon, and gradually spreads to outer regions. Though it is not very rare, the rate of survival and recovery for the patients suffering from this is relatively higher, in comparison with most other forms of cancer. Adenocarcinoma of the colon implies a malignant cancer that originates in the glands within the colon.
The individuals that are most prone to it are those who have a family history of this disease, or people who have a possibility of developing polyps in their colon or rectum. A polyp can be defined as a small growth on the layer of a mucous membrane.
Symptoms
Since this is a malignant tumor, its growth can accelerate at any time. The tumor can suddenly flare up and cause some complications in the human system, or it can lie dormant for many years. Malignant tumors generally progress for a few years before they finally break out. There have been cases of people who have been living with the tumor for 5 years but have still not showed any symptoms.
Here are the commonly seen symptoms that do crop up though.
- Rectal bleeding
- Massive changes in bowel habits and movement
- Abdominal discomfort and pain
- Bowel obstruction or constipation
- Angina and anemia
- Fatigue and shortness of breath
The size of the tumor, the stage at which its development is, and the proximity to other delicate tissues, helps a doctor determine whether the tumor will be harmful or not, and how long it will take to cure it. The method of treatment can also be decided with this knowledge in hand.
Treatment
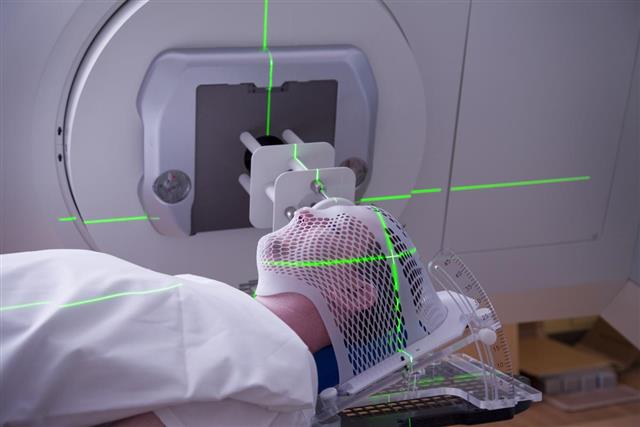
There are mainly 3 types of treatments that are available for this condition – surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. Depending on the seriousness of the tumor and its stage, one of these treatments can be administered effectively. Alternately, even a combination of two or more of these treatment methods can prove useful for a patient. Out of these 3 though, surgery is the most popular and also the most effective treatment method. The surgery that is performed for this condition is known as a radical bowel resection/partial colectomy/hemicolectomy.
In some cases, where the cancer has already begun spreading to other parts of the body, chemotherapy is carried out, in order to halt the cancer from progressing further, and also to relieve the pain. Chemotherapy simply halts the spread of the cancer, and sometimes is also combined with surgery or radiation therapy. There are some new and innovative ways also being developed to combat this condition.
The time of diagnosis and the stage of development of the cancer go a long way in determining the survival period, and even the survival rate. Though markedly higher than other forms of cancer, the survival rate is still only 50%. These rates are constantly improving though, due to several advancements that have been made. Developed countries like America, Western European countries, and Australia show the highest frequencies of this type of cancer.
Disclaimer: This HealthHearty article is for informative purposes only, and should not be used as a replacement for expert medical advice.