Cirrhosis is a chronic disease that interferes with the normal functioning of the liver. Its major cause is chronic alcoholism, apart from Hepatitis C infection. Read the following HealthHearty article to know more about this condition.
The liver is an important organ that performs several vital bodily processes. It helps to control infections by removing harmful bacteria and toxins from the blood. Liver is the processing unit for nutrients, hormones, and drugs in the body. It produces bile, which is a digestive juice that absorbs cholesterol, and helps in digestion of fats.
Cirrhosis of the liver is a serious medical condition, wherein the healthy tissue of the liver is replaced by scar tissue. This causes the liver function to deteriorate slowly. When the liver is healthy, it has the ability to replace the damaged cells with healthy cells. But once the cirrhosis reaches its end stage, the liver cannot replace the damaged cells any longer, thus giving rise to distressing symptoms, that adversely affect the quality of life of the patient.
Life Expectancy
Liver is one of the vital organs of the body. When there is any kind of irreparable or irreversible damage to the liver, the life expectancy reduces greatly. In order to assess the prognosis of a liver disease, especially cirrhosis, doctors follow the Child-Pugh score. This assessment score helps doctors determine the type of treatment, as well as the need for a possible liver transplantation. Child-Pugh score uses five clinical measures to indicate the progress of the disease. Each of these measures are scored on a scale of 1 to 3.
These five clinical measures include total bilirubin (μmol/l (mg/dl)), serum albumin (g/l), PT INR (prothrombin time), ascites (accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity), and hepatic encephalopathy (worsening of brain function due to liver’s inability to remove toxins from the blood). After calculating the score from these measures, chronic liver disease is classified in class A to C according to the Child-Pugh score. This score is given in the following table:
| Points | Class | One year survival | Two year survival |
| 5-6 | A | 100% | 85% |
| 7-9 | B | 81% | 57% |
| 10-15 | C | 45% | 35% |
According to the table, patients falling under Class A have 85% survival chances for a two-year period. Those under Class C have just 35% chances of survival after two years of diagnosis of the disease. This is because Class C indicates high-risk of death of patient. The symptoms may not appear for about 2 years after development of the condition. Some people with this condition tend to fall gravely sick within 3 to 5 years. After the initial symptoms like itching disappear and jaundice develops, it can be concluded that the disease has reached its advanced stage. Thus the life expectancy is just about 34-66% for 10 years.
Causes
The major reasons behind this condition is chronic alcoholism and chronic hepatitis C. Nowadays, obesity is also becoming a factor. It is not a short-term occurrence. One suffers from this condition due to years of chronic alcohol abuse or chronic injury to liver. It can also occur due to primary biliary cirrhosis, cystic fibrosis, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, sclerosing cholangitis, galactosemia, schistosomiasis, glycogen storage disease, Wilson’s disease, and other liver disorders. One can improve their life expectancy by abstinence from alcohol, healthy diet, and liver transplant in case of severe liver cirrhosis.
Symptoms
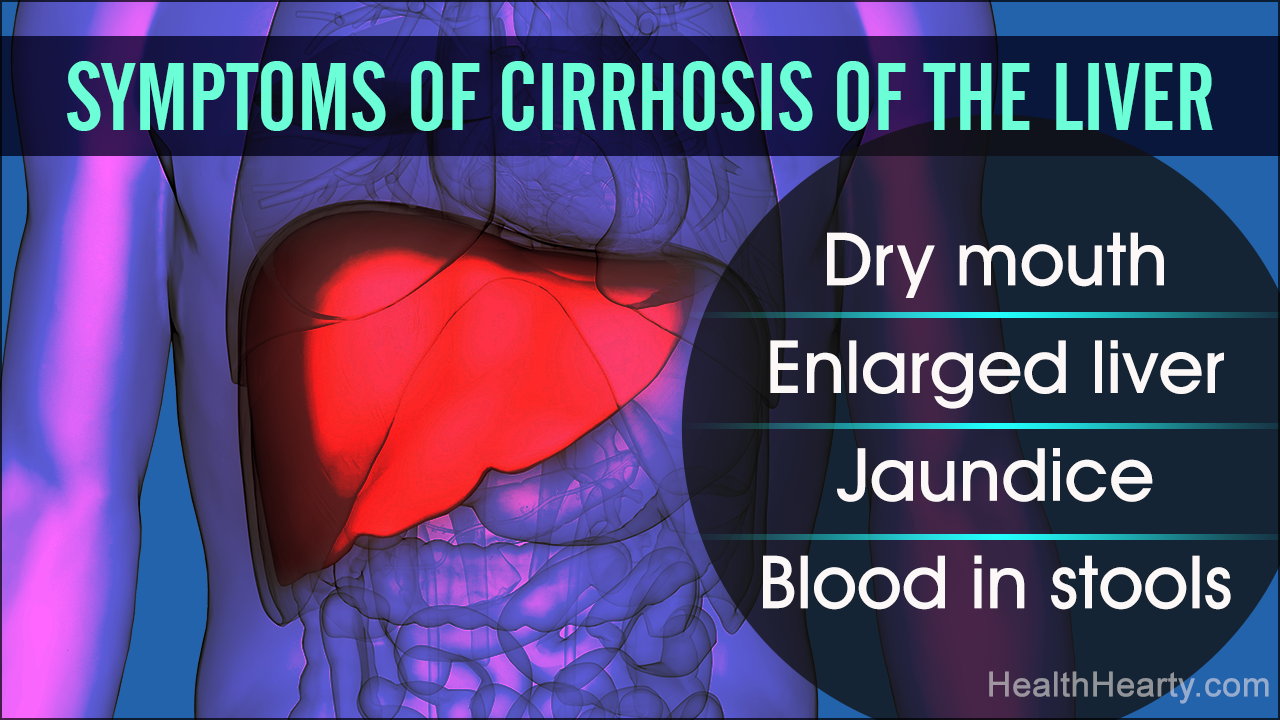
In the initial stage of cirrhosis, the patient may suffer from:
- Fatigue
- Dry mouth
- Jaundice
- Enlarged liver
- Tenderness of the upper right abdomen
- Loss of appetite
- Itchy skin
- Edema and swelling in the ankles, legs and abdomen
- Light colored stools and brownish or orange-colored urine
- Confusion, disorientation
- Blood in stools
- Fever
After the first stage, the liver disease progresses to the second stage. In the second stage, the abnormal tissues form stiff bands of connective tissue called fibrosis. This fibrosis and inflammation spreads to the portal areas and periportal space of the liver. In the stage three, the areas of fibrosis merge together, thereby causing enlargement of the liver. There is liver degradation that leads to reduced functioning of the liver. Thus, the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins and fats is adversely affected. The final liver cirrhosis stage is stage four. There are very less chances of survival at this stage. Only a liver transplant can save the patient. Thus, the life expectancy is less than 10 years for people in last stage, also known as symptomatic stage of cirrhosis.
Treatment
The treatment is aimed at slowing down the progression of the disease, and stopping further damage to liver cells. Complete abstinence from alcohol is integral to the treatment. In case of hepatitis, the doctor may recommend the use of steroids and antiviral drugs. The treatment would vary, if cirrhosis of liver is caused by Wilson’s disease, hemochromatosis, or other autoimmune diseases.
To control the symptoms of edema and ascites, a low-salt diet has to be followed. Diuretics may be advised to reduce accumulation of fluids. Laxatives may be given to help adsorb the toxins and remove them from the intestines. In case of severe cirrhosis, the doctor may advise liver transplantation.
Diet
Following a low-fat diet that includes, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains might help. Obese people need to reduce their weight, and maintain a healthy weight according to their height and age. Affected individuals should reduce the intake of salty food, and abstain from alcohol consumption.
It has been observed that 85% of people undergoing liver transplantation reach the five-year survival rates. You should reduce the chances of liver damage to prevent the onset of this condition. When the initial stage is diagnosed, make some lifestyle changes. This is because class A has the most favorable prognosis.
Disclaimer: The information in this article is not intended to replace the medical advice of your doctor or health care provider. Please consult a health care provider for advice regarding any specific medical condition.