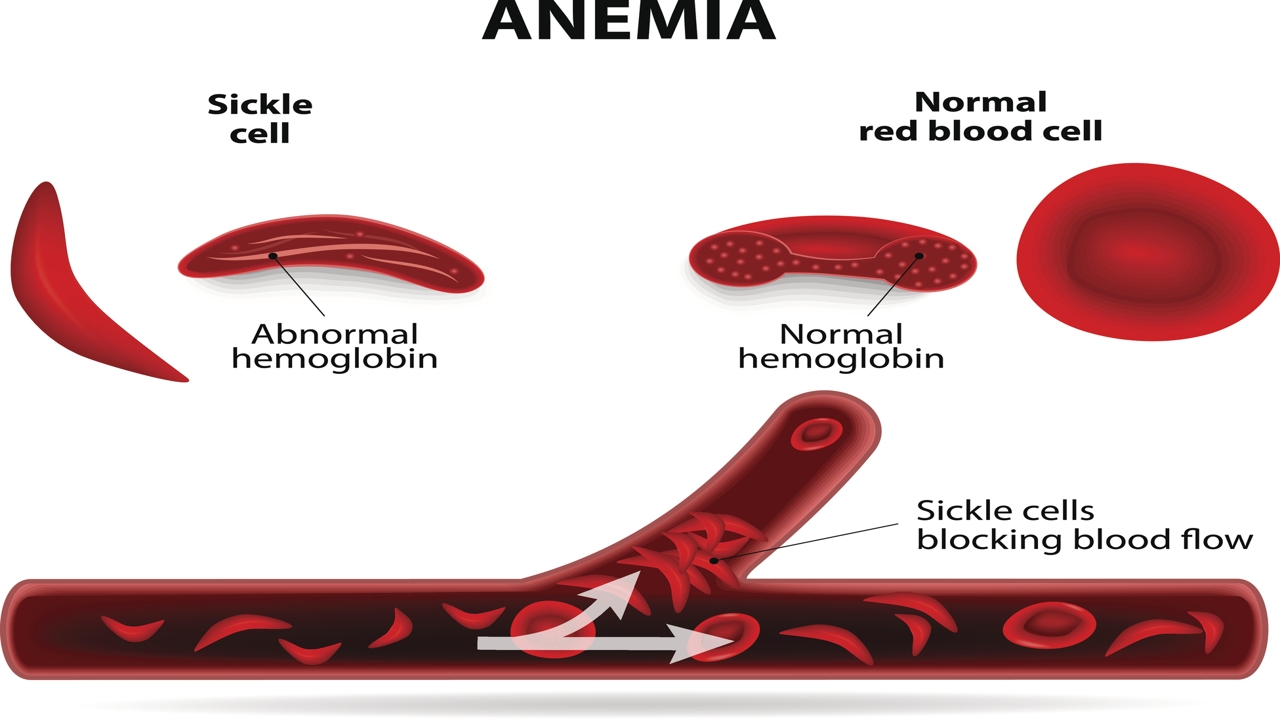
Sickle cell anemia is an inherited condition, where the red blood corpuscles become sickle shaped or ‘C’ shaped. Here’s more about its causes and symptoms.
Normally, red blood cells are round and smooth. They look like a doughnut without the hole. They move very easily through the blood vessels and help carry oxygen to the various parts of the body. However, when these cells become sickle shaped, they tend to become stiff and sticky. They form clumps and stick to the sides of the blood vessels. This causes a blockage in the flow of blood to the various parts of the body. Eventually, this leads to pain, infections, and damage to various organs of the body.
Sickle cell anemia is an inherited disease. If the child gets the gene from both the parents, it is born with this condition. But if only one of the parents has the gene, then the child doesn’t get the disease. However, it becomes a carrier of the disease.
The symptoms do not manifest until the baby is approximately 4 months old.
- Anemia – Generally, all the symptoms of anemia are present in those suffering from this condition. The baby may need to be hospitalized for treatment. The common signs include fatigue, pale skin, yellowish skin, and shortness of breath.
- Pain – There is reduction or stoppage of blood flow to the various organs of the body. This causes chronic or acute pain, which can range from mild to severe. It can last from weeks to months. This can also limit daily activities, and can be draining on the person, physically and mentally. An episode of sickle cell crisis can occur at least once a year, and in some cases, as often as 15 times a year.
- Swelling in Hands and Feet – Due to blockages in the blood vessels, there can be a painful swelling in the hands and the feet.
- Infections – Patients become prone to several infections because of improper blood supply.
- Spleen Infections – The spleen is located in the abdomen. The function of the spleen is to filter out abnormal red blood cells. With patients suffering from this particular condition, the spleen ends up trapping many red blood cells and becomes swollen. With too many abnormal red blood cells, it may become clogged and stop working.
- Delayed Growth – Due to insufficient blood flow to the entire body, patients often experience delayed growth.
- Stroke – Improper blood flow leaves the patient susceptible to a stroke.
- Eye Problems – Patients may suffer from eye problems because the retina doesn’t get enough blood. This may even lead to blindness.
- Multiple Organ Failure – Due to insufficient blood supply and susceptibility to infections, patients can be prone to several organs failing at one time.
As such, there is no cure for sickle cell anemia. However, the pain can be treated using painkillers. Often, liquids are supplied to the body via the mouth or the veins, to avoid dehydration.
Children suffering from this disease need to visit their doctor regularly. Until the age of 5 years, a daily dose of penicillin is given to them. Folic acid or folate may also be prescribed. Nowadays, nitric oxide is also used to make the sickle cells less sticky.
This condition affects millions of people globally. But with the treatments available nowadays, thanks to the miracles of modern medicine, affected patients can live long and fruitful lives.
Disclaimer: This HealthHearty article is for informative purposes only, and should not be replaced for the advice of a medical professional.


