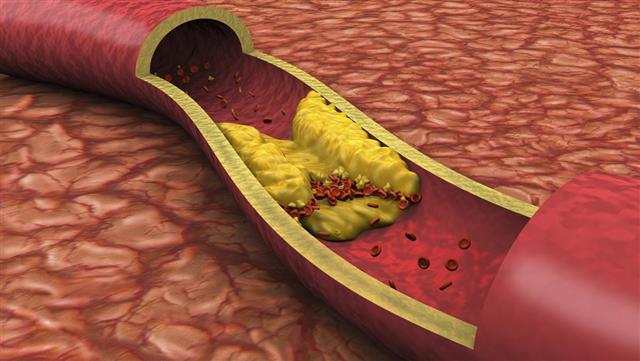
An arterial blockage in the heart is a buildup of high fat and cholesterol content within the blood vessels in the body. This article throws light on the various symptoms of arterial blockage in the heart.
Do you know that coronary heart disease is one of the leading causes of death in America? The coronary heart disease is a direct result of the arterial blockage in the heart. The heart is a vital organ of the body that is responsible for pumping more than three thousand gallons of blood every day.
The continuous supply of blood keeps it healthy and functioning properly. However, when there is a buildup of cholesterol and fatty deposits inside the walls of the arteries of the heart, it leads to the restriction of blood flow in the heart either by physically blocking the flow or altering the function of the arteries. This buildup of plaque inside the inner walls of the arteries is known as Atherosclerosis or arterial blockage in the heart.
What Causes Arterial Blockage in the Heart
The arteries in the heart are shaped like hollow tubes which are smooth and elastic. These tubes allow the easy flow of blood in the arteries. The buildup of plaque which is made up of cholesterol, inflammatory cells, calcium and proteins in the blood can lead to the narrowing and subsequent clogging of these coronary arteries.
The plaque not only stops the blood flow but also causes damage to the artery walls due to the hardening of the arteries. The plaque which is hard on the outside and soft inside may develop a crack or a tear. This causes the soft, sticky fat layer to come outside which in turn can lead to the platelets in the blood to stick to the surface, resulting in blood clots. This causes even more blockage in the arteries of the heart.
Without the adequate blood flow in the heart, the heart becomes starved of the essential oxygen. This condition is referred to as ischemia which is characterized by sharp chest pain or angina. In cases where the blood flow in the heart is restricted completely, an injury to the heart muscle or heart attacks can happen. Risk of heart attacks are increased when blood clots cut off the blood supply in the heart muscles. In certain cases, the heart may develop new blood vessels that aid in the blood flow in the heart. This is known as collateral circulation.
Angina (Chest Pain): When the muscles in the heart are cramped, the most common symptom is chest pain in the left side. Also known as angina or angina pectoris, this is often a warning sign of clogged arteries in the heart. Most people confuse it with indigestion or heartburn as it produces similar symptoms such as:
- Tightness or heaviness in the chest
- Pressure
- Burning sensation in the chest
- Numbness
- Radiating pain to the left shoulder, arms, neck and jaw
The angina symptoms usually last for not more than a few minutes especially when engaged in certain stressful activity. With rest and medications the chest pain subsides. This is known as stable angina. However, when the blood clot forms around the arteries and there is severe constriction of the arteries, severe and prolonged chest pain occurs. This is known as unstable angina which may be a warning signal of an heart attack.
Shortness of Breath: When the heart does not pump enough blood, you may have difficulty breathing especially when engaged in certain strenuous activity. This can be accompanied by nausea, extreme weakness and fatigue.
Irregular Heartbeat: Irregular heartbeat with palpitations or a faster heartbeat can indicate an arterial blockage. In women, a sign of clogged arteries is an unusually rapid heartbeat.
Heart Attack: In many cases clogged arteries may not produce any symptoms but may lead to a heart attack. The heart attack symptoms commonly experienced include crushing pain in the left side of your chest, pain in shoulders and arms along with shortness of breath, cold sweat, nausea, vomiting and dizziness. Women may suffer from nausea and pain in the jaws. Heart attacks can cause permanent damage to the heart muscles or eve lead to death in certain cases.
There are many causes that contribute to the increased risk of arterial blockage by plaque including:
- High cholesterol levels
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Smoking and alcohol
- Lack of physical activity
- Obesity
- Hereditary factors
- Age (Often seen in elderly people over the age of 65 years)
- Stress and Tension
- Diet rich in saturated fats
- Gender (men are prone to suffering from clogged arteries)
To diagnose blocked arteries in the heart, diagnostic tests like electrocardiogram, blood tests and exercise stress tests may be done. The tests help the doctor in understanding the extent of blockage in the arteries and the best way to treat it.
Lifestyle Changes: Changes in the diet, quitting smoking, controlling your blood pressure and sugar levels are some of the common lifestyle modifications To keep your weight in check eat healthy foods and exercise regularly.
Medications: To reduce the chest pain, nitroglycerin tablets or sprays are prescribed. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and beta blockers can be used for controlling the blood pressure. To prevent artery blockage due to blood clots anticoagulants like aspirin are prescribed. Cholesterol lowering medications and calcium channel blockers are some other medications used to treat arterial blockage.
Surgical Options
→ Balloon Angioplasty: A thin tube or catheter is inserted into the blood vessel. A tiny balloon is placed on the tip of the catheter which is inserted in the blocked artery and inflated. This opens up the artery by pressing the plaque to the walls of the artery and allows the blood to flow without any hindrance. Sometimes a stent or a wire mesh is placed within this blockage to prevent the artery from blocking again.
→ Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): An open chest surgical procedure, the CABG utilizes a section of a healthy blood vessel from any part of the body like the patient’s leg vein to make a detour or bypass the partial or complete blockage in the coronary artery system.
Coronary heart disease cause by arterial blockage affects millions of people around the world. Minimize the risks of the arterial blockage and the subsequent problems like heart attacks by staying healthy and fit. Avoid high cholesterol foods, and exercise on a regular basis. If you have history of heart blockage or coronary problems then do talk to a doctor before joining any fitness program.
Disclaimer: This article is for informative purposes only, and should not be considered as a substitute for professional medical advice.