In this article, we’ll have a look at the symptoms and treatment options of a carotid artery blockage.
What is a Carotid Artery Blockage?
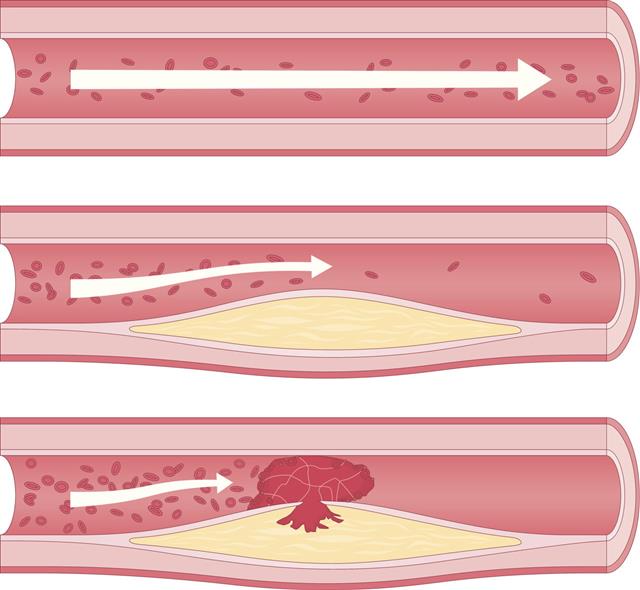
Carotid artery blockage, also known as carotid artery stenosis, is the constriction of the inner surface of the carotid artery due to buildup of plaque.
In simpler terms, a carotid artery blockage is a result of the blood vessels in the neck getting blocked due to the buildup of plaque on the arterial walls.
The carotid arteries are two large blood vessels on each side of the neck, and they supply blood, oxygen, and other vital nutrients to the brain in order to sustain life.
They branch off from the aorta, travel through the heart, and then extend from the neck, upwards. The pulse which throbs on the sides of the neck indicates the carotid artery.
A blockage in these arteries is caused by atherosclerosis, which is a progressive vascular disease that causes accumulation of fatty substances, calcium, fibrin, cellular waste, and cholesterol, also known as plaque, inside the walls of the arteries. This leads to the narrowing of the walls of the arteries, and causes the condition known as carotid artery disease.
Risk of Carotid Artery Blockage
It is important to note that carotid artery blockage is one of the major contributing factors for strokes. This is because, over time, when the plaque hardens and narrows down the arteries completely, the blood supply and oxygen to the brain is restricted. Without proper blood or oxygen supply, the cells in the brain start to die. This leads to the loss of brain functioning, and permanent brain damage or death of an individual.
In certain cases, plaque buildup in the arteries can break off, travel through the bloodstream, and get lodged in some blood vessels in the brain. This can trigger off a transient ischemic attack. It is thus vital to watch out for the symptoms of a carotid artery blockage, so that necessary steps can be taken before the individual’s condition worsens.
Common Symptoms
A carotid artery blockage can be asymptomatic in the initial stages. When there is a significant amount of plaque buildup in the arteries, but it does not hamper the blood flow too much, then there may not be any symptoms of the blockage. However, as the plaque buildup increases, the blood flow can be totally cut off, leading to a transient ischemic attack or a brain stroke.
In case the person suffers from a transient ischemic attack, then he or she can display certain symptoms like:
- Weakness or inability to move the arms and legs.
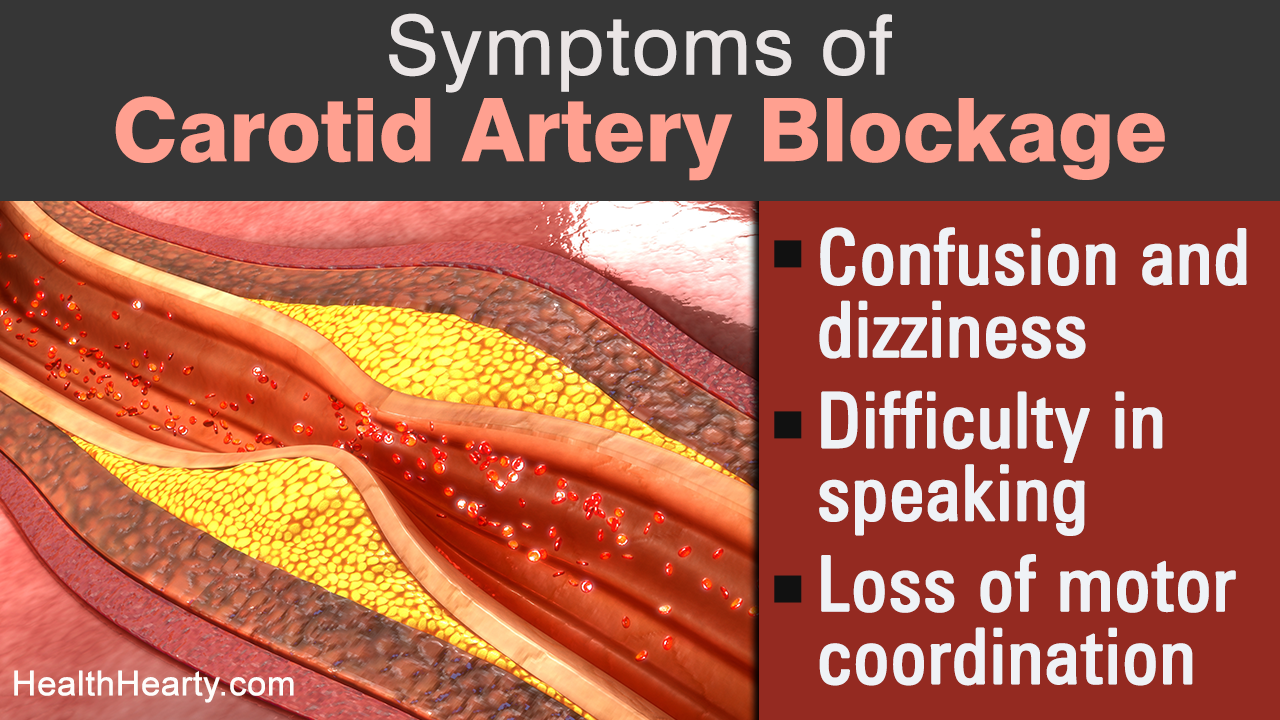
- Confusion and dizziness.
- Headaches.
- Fainting.
- Difficulty in speaking, slurring words.
- Loss of motor coordination.
- Sudden and temporary numbness in the face.
- Temporary loss of vision.
- Difficulty in swallowing.
- Tingling sensation in the arms, which may radiate to other body parts as well.
In case the person suffers from a stroke, then along with these symptoms, he or she may lose other vital body functions too, like memory and thinking, eating, bladder functioning, and control over emotions.
Diagnosis

If any of the symptoms are observed, one must seek medical help immediately. Unless a stroke or paralysis has occurred, most doctors first rely on checking the pulse through a stethoscope for any unusual sounds produced as the blood gushes past the blockage. Once the site of the blockage is identified, a duplex ultrasound test is used to detect it and measure the quantity of blood flowing through the artery.
Another diagnostic test known as a cerebral angiogram, is also used to determine the intensity of the blockage. A special dye (usually blue or black in color) is injected into the artery, and an X-ray is taken. The results of the X-ray show the exact location and size of the blockage, which is determined by the path that the dye has taken.
If it is a case of a stroke or paralysis, then diagnostic tests like a CT Scan, Carotid Duplex Scanning, Transcranial Doppler (TCD), MRI Scan, Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA), Xenon CT Scanning, Radionuclide SPECT Scanning, Cerebral Angiography, and PET Scanning and Transesophageal Echocardiography, may be recommended by the physician.
Treatment Options
The treatment of the artery blockage depends upon various factors, including age, health, and medical history of the patient. The signs and symptoms displayed, extent of the blockage, and tolerance to various surgical procedures and medications, can determine the course of treatment. There are three ways in which a carotid artery blockage can be treated – medications, changes in lifestyle, and surgical measures.
Lifestyle Modifications
Apart from age and a family history of the disease, people with elevated blood pressure, excess cholesterol, and diabetes are at the risk of suffering from this disease. Smoking, a diet rich in saturated fats, a sedentary lifestyle, and obesity, can further aggravate the problem.
To keep the plaque buildup in control, quit smoking and eat food that is low in saturated and trans fats. Maintain your weight by following a healthy diet and exercising regularly. To effectively lower the chances of a stroke, it is important to keep your blood pressure and diabetes in check.
Medications
In case the plaque buildup in the arteries is less than sixty percent, then certain medications may be prescribed to delay the clot formation in the arteries. Antiplatelet medications like clopidogrel and dipyridamole can be prescribed to reduce the blood clot formation. These medications reduce the ability of the platelets to gel together and form clots in the arteries. Similarly, anticoagulant medications or blood thinners can be used to restrict the clotting.
If the doctor suspects high blood pressure, then antihypertensives may be recommended for keeping the blood pressure in check. For excess fats in the blood, antihyperlipidemics like pravastatin and simvastatin may be recommended. These medications have known to reduce the thickness of the artery walls and increase the opening of the artery.
Surgical Options
In case the plaque buildup has caused a blockage of around seventy percent or more, or the patient has already suffered a minor stroke, then surgical treatment options have to be considered. In case of blockage of around 50% to 69%, the doctors may consider surgery based on the person’s age and health condition.
Carotid Angioplasty with Stent

Apart from endarterectomy, a newer procedure for treating a carotid blockage is carotid angioplasty with stenting. A minimally-invasive procedure, carotid angioplasty is done by passing a catheter from the blood vessels in the groin to the carotid artery. Once this hollow tube is in place, a balloon is inflated to open up the artery, after which a stent is put in place.
A stent is a small wire mesh tube which holds the artery open and provides support therein. To prevent any plaque bits from moving to other parts during the procedure, the surgeon places an embolic filter which catches any debris during the process.
Endarterectomy
This is the standard surgical procedure used for treating a carotid blockage, wherein the fatty plaque in the carotid artery is removed by making an incision in the neck. Once the incision is made and the artery is exposed, the surgeon clamps the artery and opens it up lengthwise. Now the plaque needs to be physically removed by scraping it out. Once this is done, the artery is enlarged with a diamond-shaped patch, and is stitched together.
To prevent the chances of a fatal stroke or paralysis, it is necessary to watch out for the symptoms of the blockage and opt for immediate treatment. To avoid a carotid artery blockage, it is important to keep yourself healthy and fit. Quitting alcohol and tobacco, following a diet that is low in fat and cholesterol, along with regular exercise, will go a long way in avoiding such a condition from arising.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only, and should not be used as a replacement for professional medical advice.